Acute Vs Chronic Folliculitis: What Beauticians Need to Know
In the world of beauty and skincare, folliculitis is a term that is unfortunately all too familiar. As a beautician, you're likely to encounter both acute and chronic folliculitis in your practice. Both conditions can affect your clients' confidence and comfort, and knowing the differences between them can be crucial in providing the best care. This article delves into the nuances of acute vs chronic folliculitis, a topic that is essential for any beauty professional to master.
What is Folliculitis?
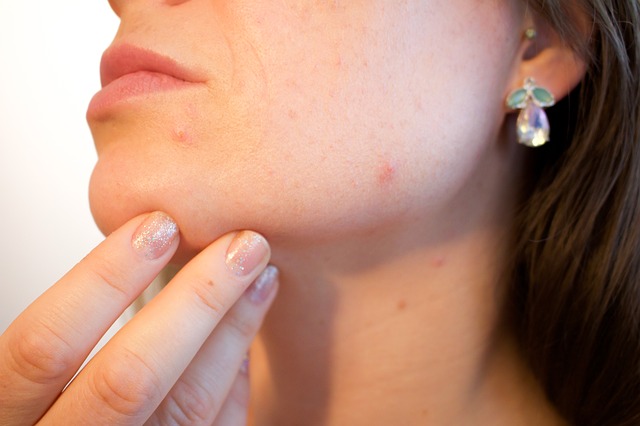
Folliculitis is the inflammation of hair follicles, presenting as small, white-headed pimples around hair follicles. While it may seem like a minor skin issue, it can lead to discomfort and anxiety for clients, especially if it progresses into more severe forms. Knowing the basics of this condition can help beauticians guide their clients towards effective management strategies. For a detailed medical overview, check the Patient Info Folliculitis Guide.
The Dichotomy: Acute vs Chronic Folliculitis
Acute folliculitis manifests as sudden outbreaks, often due to infections by bacteria like Staphylococcus. This form typically resolves with appropriate treatment in a few days to weeks. In contrast, chronic folliculitis persists over a long period, possibly due to recurring infections or underlying health issues. Recognizing which type you're dealing with is key to implementing a suitable treatment strategy.
Causes and Triggers
The causes of acute folliculitis could be traced to recent activities such as waxing, shaving, or hot tub use, which can introduce bacteria to compromised skin. Meanwhile, chronic folliculitis may be linked to factors such as immune system deficiencies or ongoing exposure to irritants. To understand more about irritant folliculitis and its causes, visit Livana Natural's blog.
Impact on Beauty and Skincare Routines
For beauticians, understanding these conditions helps in advising clients on the best skincare practices. This could range from recommending gentle skin cleaning products to advising on safe hair-removal techniques. Be sure to refer your clients to our article on how to clean skin after beach visits, which discusses maintaining skin health in challenging environments.
Management and Prevention Strategies
Acute cases are often managed with topical antibiotics, which reduce inflammation and clear up infections quickly. Chronic folliculitis, however, may require a more comprehensive approach, including lifestyle adjustments and possibly systemic treatments. Here, the role of a beautician can be pivotal in ensuring that clients stick to a skincare regime that minimizes outbreaks. Learn more about Demodex folliculitis as part of managing chronic conditions.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While beauticians play a key role in client education and initial care, severe or persistent cases of folliculitis may require medical intervention. Encouraging clients to consult healthcare professionals when home remedies aren't effective is a responsible practice. The National Library of Medicine provides guidance on when to seek medical help for folliculitis.
Client Support and Communication
Building trust with your clients involves not only providing effective treatments but also offering ongoing support. Clients grappling with folliculitis will appreciate advice on soothing irritated skin, selecting non-irritating cosmetics, and understanding treatment options. Our resource on Sycosis barbae can further help in managing client concerns effectively.
FAQ
What is the primary difference between acute and chronic folliculitis?
Acute folliculitis appears suddenly and typically resolves quickly with treatment, while chronic folliculitis persists over time and may recur frequently.
How can beauticians assist clients with folliculitis?
Beauticians can offer advice on gentle skincare routines, recommend non-irritating products, and suggest when to seek medical advice for persistent cases.
Are there specific treatments for chronic folliculitis?
Management of chronic folliculitis may include topical therapies, antibiotics, and in some cases, lifestyle adjustments to minimize irritant exposure and boost immune response.

